

Wireshark provides the flexibility to configure packet that need to be captured with various capture options. This doesn’t give the flexibility to see on which interface the packets are active users can configure the capture options by double clicking on the interface or by clicking on Capture Options: In Start options, users can multiselect or select the interface displayed in the list and then click on Start. A few of them are shown in the following diagram: The Interface name tells the network type by looking at the name of interface the user should understand what network the capture setup is associated with-for example, eth0 stands for Ethernet. If you want to capture packets on loopback ( 127.0.0.1), select the interface lo0. Capturing packets with Interface ListsĬlick on Interface List Wireshark will show a list of available network interfaces in the system and which one is active, by showing packets going in and out of the Interface, as shown in the following screenshot:Ĭhoose the right (live) interfaces and click on the Start button to start capturing packets. We will cover each capturing option in detail one by one. Provides various options for capturing and displaying packets You can choose an interface from the list and start capturing packets Opens up a live list of capture interfaces, and counts the incoming/outgoing packets
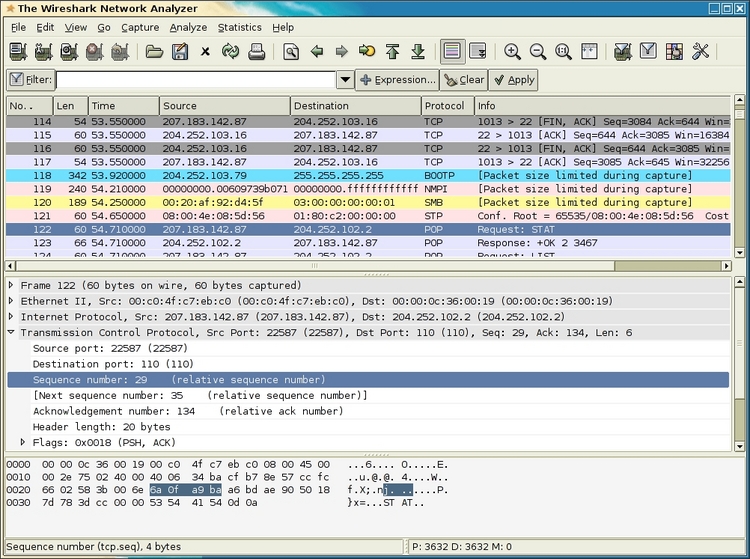
The following table explains the various options that we have in the Start screen: When Wireshark starts it launches the following screen and provides the following ways to capture packets: Start Wireshark by clicking on the Wireshark icon or type Wireshark in the command line. (For more resources related to this topic, see here.) Guide to capturing packets
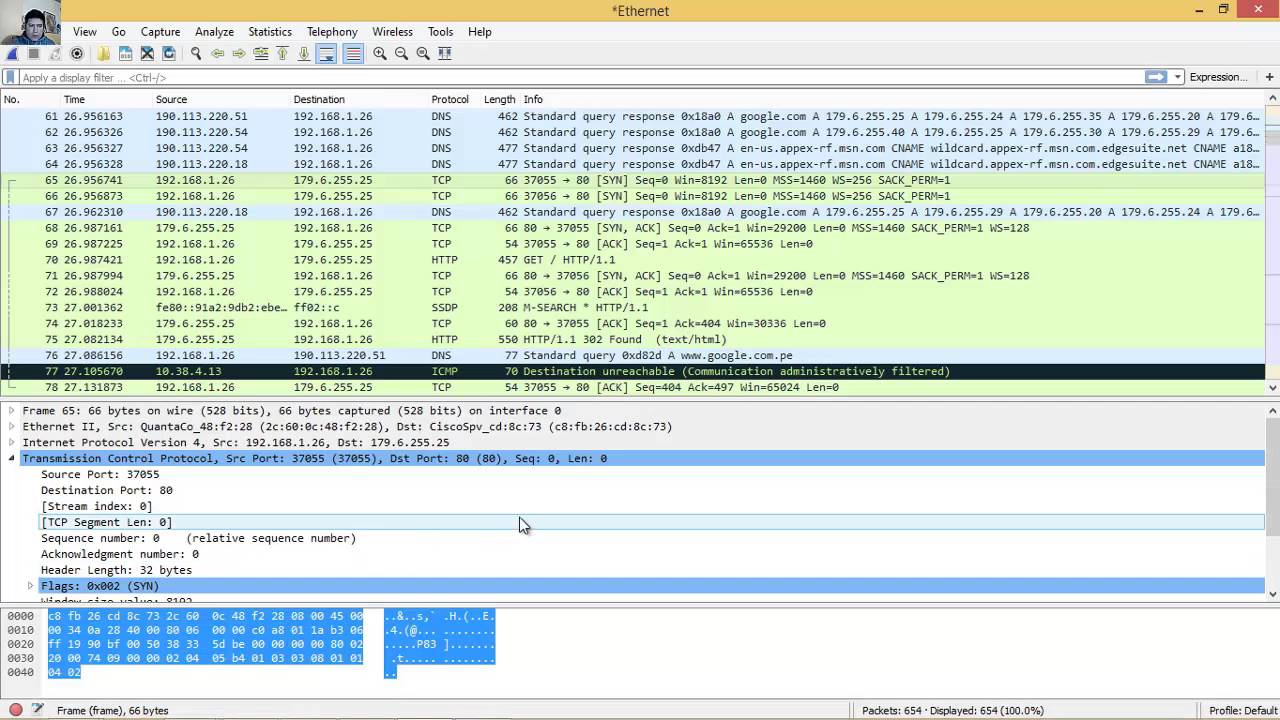

In this article by Anish Nath, author of the book Packet Analysis with Wireshark, we will learn about the Wireshark GUI features, and see how it helps in capturing and analyzing packets effectively, by covering the following topics:


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
